What Are the Different SAP Ariba Solutions? Part 2 is the second part of the series, In this blog, I will explain the What is Ariba Sourcing solution—its purpose, need, key features, uses, and much more.
Before diving into this topic, please refer to “What Are the Different SAP Ariba Solutions? Part 1” for better clarity and understanding, as each Ariba solution is closely connected to the others.
Table of Contents
What is Ariba Sourcing
Ariba Sourcing is one of the important solutions of SAP Ariba. If anyone asks what the use of this solution is, in simple words I can say: this solution is specially designed for situations where a company has multiple suppliers and becomes confused about which supplier can give the best deal. In such cases, Ariba Sourcing plays a crucial role.
Ariba Sourcing Architecture:
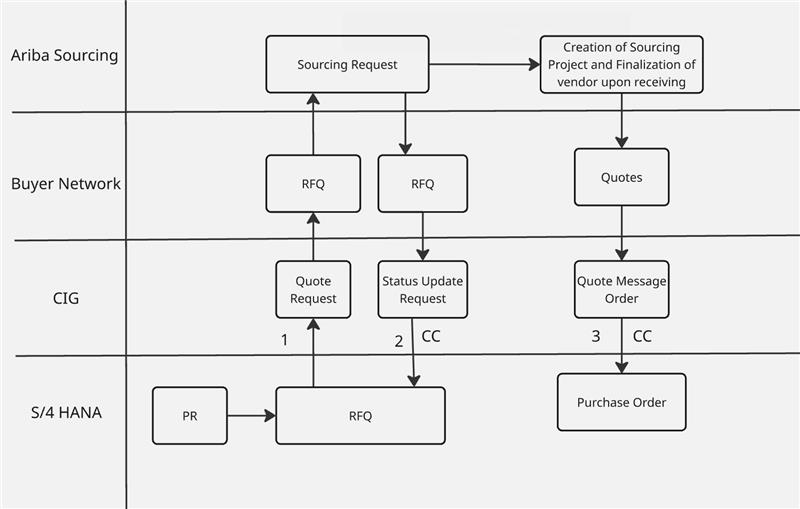
- In the SAP Ariba Sourcing architecture, the starting point is SAP S/4HANA. First, we create a PR, and with respect to that PR, an RFQ will be created. After the RFQ is created, it will first go to CIG as the document type Quote Request, then it will go to the Buyer Network, and finally it will reach Ariba. In Ariba, a Sourcing Request will be created with respect to the RFQ.
- Now that the RFQ has successfully reached Ariba and the Sourcing Request is also created, Ariba will send a confirmation to S/4HANA. As a result, a Status Update Request will be generated in CIG, and then it will be updated in S/4HANA through the Cloud Connector.
After Sourcing request buyer will create a Sourcing Project, While creating an project he need to select event type weather it is RFP,RFI and Auction let me explain what is meaning of these terms.
i) RFI — Request for Information
RFI is used when a company wants information from suppliers.
Why it is used:
To understand supplier capabilities
To check supplier qualifications
To gather general details before starting sourcing
To shortlist potential suppliers
Simple example:
A company wants to start working with new logistics suppliers, but first they want to know:
Service areas,Delivery capacity,Company profile,Certifications
So they send an RFI to collect information.
ii) RFP — Request for Proposal
RFP is used when a company wants a detailed proposal including pricing, technical details, and terms.
Why it is used:
To get complete solutions from suppliers
To compare supplier pricing and approach
To understand total cost and value
To select the best supplier based on multiple criteria
iii) Auction (eAuction)
An Auction is a real-time competitive bidding event where suppliers continuously quote prices, especially lower prices.
Why it is used:
To get the lowest possible price
To create price competition
To make fast, transparent decisions
Simple example:
A buyer hosts a reverse auction for office chairs.
Suppliers join the bidding room and keep reducing their prices in real time.
The buyer gets the best possible deal.
So, the above are the types of events. If a buyer decides to conduct an Auction, they will run the Auction among suppliers to get the best deal. After finalizing the project, the buyer will award it to the supplier who wins the Auction.
- Now, the buyer will send the awarded supplier details to S/4HANA so that the awarded quotes will be generated in the Buyer Network. Then, in CIG, the document will be sent as a Quote Message Order, and these quotes will be sent to S/4HANA through the Cloud Connector. When the quotes reach S/4HANA, the Purchase Order will be created.
Important points to keep in mind
- CIG stands for Cloud Integration Gateway. It is a central platform that handles all integration activities. CIG is the older name — the current name is Managed Gateway for Spend Management and Business Network. In this blog, we continue to use the name CIG because many people still commonly refer to it as CIG.
- Message type of RFQ(Quote Request) is IDOC .Message type of Status Update Request is Webservice. Message type of Quote Message Order is Webservice.
- Cloud Connector (CC) acts as a firewall and secure tunnel between CIG and S/4HANA. Whenever data flows from CIG to S/4HANA, it always passes through the Cloud Connector
- Always remember, S/4HANA understands XML, while Ariba understands cXML. So whenever data goes from S/4HANA to Ariba, CIG converts the data from XML to cXML. Similarly, when data goes from Ariba to S/4HANA, CIG converts the data from cXML to XML.
CIG plays a crucial role in data transfer between both systems.
